The importance of decentralization in Ethereum‘s development, spearheaded by its founder Vitalik Buterin, has been a recurring theme. A new idea that is picking up steam is the concept of “anti-correlation penalties,” which is designed to combat the centralizing effects of economies of scale within Ethereum‘s staking system.
To boost the decentralization of Ethereum’s staking system, researcher Toni Wahrstätter suggests introducing anti-correlation penalties as a solution. The purpose of these penalties is to weaken the benefits of having large staking pools, which now encourage centralization among stakers.
Toni Wahrstätter did an outstanding job building upon and broadening the exploration I initiated last month concerning correlations in cross-validation and incentivizing validators to promote decentralization.
— vitalik.eth (@VitalikButerin) April 9, 2024
In a recent examination, the proposition is explained with clarity, revealing how anti-correlation penalties can affect staking managers and software developers, thereby enhancing the importance of their functions in fostering a more dispersed system.
Economies of Scale and Ethereum Centralization
At present, stakeholders enjoy the perks of economies of scale, including improved network connections, dependable hardware, and skilled infrastructure management. Nevertheless, this advantage can result in centralization, allowing bigger staking operators to control the network using their extensive resources.
In order to offset the benefits of larger economies, it’s vital to implement measures that support decentralization.
Understanding Anti-Correlation Penalties
According to Wahrstätter’s explanation, the notion of anti-correlation penalties aims to offset the benefits of having economies of scale. In this setup, when a solitary validator operator encounters downtime on a single machine, it results in simultaneous disruption for all validators involved.
This occurrence leads to interconnected risks, where the collapse of one validator can cause other validators managed by the same entity to fail as well. Anti-correlation penalties are designed to deter individuals from taking advantage of economies of scale by imposing penalties for related risks.
Vitalik Buterin’s suggested formula for anti-correlation penalties, as reported by Coinspeaker, calculates penalties based on the difference between a validator’s current and average number of missed attestations over a certain period. If a validator misses more attestations than the average in a given slot, they will face a penalty. This system aims to uncover and penalize hidden coordination among validators, thereby decreasing the influence of centralization forces.
Impact on Staking Operators and Client Implementations
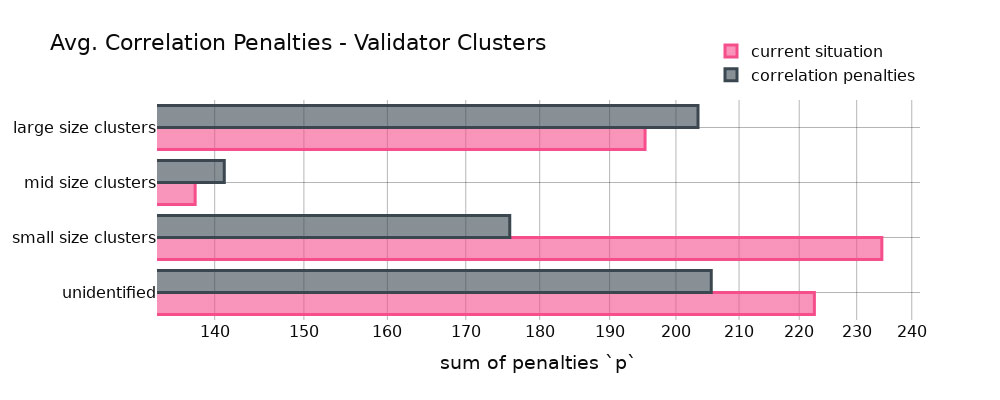
Average Correlation Penalties on Different Validator Clusters. Photo: Ethresear.ch
A study was performed on a dataset encompassing all occurrences within a particular time frame, totaling around 40 days and approximately 9.3 billion validator actions. Wahrstätter conducted the quantitative examination of this data.
Vitalik Buterin’s suggested formula for penalties on staking operators was tested through simulation in this analysis. The findings revealed that larger clusters would face increased penalties, whereas smaller clusters would experience relief from lower penalties.
In a similar vein, the research looked into how anti-correlation penalties affected various client setups. The findings revealed only small differences from the present penalty scheme, as certain clients faced increased penalties whereas others enjoyed less severe ones due to these adjustments.
Read More
- DBD July 2025 roadmap – The Walking Dead rumors, PTB for new Survivors, big QoL updates, skins and more
- Here Are All of Taylor Swift’s Albums in Order of Release Date (2025 Update)
- PUBG Mobile Sniper Tier List (2025): All Sniper Rifles, Ranked
- Delta Force Redeem Codes (January 2025)
- [Guild War V32] Cultivation: Mortal to Immortal Codes (June 2025)
- Stellar Blade New Update 1.012 on PS5 and PC Adds a Free Gift to All Gamers; Makes Hard Mode Easier to Access
- COD Mobile Sniper Tier List Season 4 (2025): The Meta Sniper And Marksman Rifles To Use This Season
- Aaron Taylor-Johnson Debuts New Look at 28 Years Later London Photocall
- How to Update PUBG Mobile on Android, iOS and PC
- Best Heavy Tanks in World of Tanks Blitz (2025)
2024-04-09 18:06